Mechanical to Electrical Energy
Intial Construction & Brainstorm
During my stay in India in the summer of 2011, I collected a few spare parts from a carpentry shop and a local garage. These items included 2 PVC pipes, nuts, bolts, 2 rotor blades of a broken toy helicopter, 2 motors of a broken toy car. I got the pipes attached in a T shape, using one pipe as the apparatus holder and the other as the stand.
The electric motors were placed at the open ends of the apparatus holder. The rotor blades of the toy helicopter were then attached to the shaft of respective electric motors.
AIM:
To apply my knowledge, of physical sciences, attained from my school resources about :
i)Magnetic flux
ii)Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction
iii)Lenz’s Law
iv)Electric Motor and Generator
v)Induced Current
vi)Law of conservation of energy
and demonstrate the conversion of mechanical to electrical energy.
APPARATUS:
2 PVC pipes, a powerful air blower, Light Emitting Diodes, nuts, bolts, cardboard, 2 rotor blades of a broken toy helicopter, 2 motors of a broken toy car.
BLOCK DIAGRAM

Figure-1
The air used in this project is replaced by pressurized steam in the thermal power plants. We haven’t used steam to keep the electrical apparatus as dry as possible. We have also reversed the functioning of an electric motor to generate induced current in the circuit. This current lights the LED lamps.
PROCEDURE:
1.Place the T shaped apparatus on the cardboard and attach its lower end to the board with the help of screws and bolts.
2.The air blower is placed in front of the apparatus such that the air duct is in line with the rotor blades at the ends of the PVC pipe.
3. As the air impinges on the rotor blades the connected shaft of the electrical motor also rotates inside the apparatus.
4.This causes a change in magnetic flux within the electric motor thereby inducing an EMF (potential difference).
5.The charged particles move under the influence of the EMF and hence an induced electric current is set up in the circuit.
6.This current lights up the Light Emitting Diodes.
WORKING PRINCIPLES
1)Magnetic flux (ΦB):
Magnetic flux through a plane of area A placed in uniform magnetic field B can be written as
ΦB = B . A = B A cosθ
Where θ is the angle between B and A.
A is the area vector and is defined as a vector whose magnitude is A and whose direction is perpendicular to the plane.
A)MECHANICAL ENERGY
The function of air blower was to rotate the fins attached at the 2 ends of the pipe. This rotation is due the angular force (torque) applied by the air on the rotor fins. The shafts of the electric motors also rotate as they are connected to these rotor blades. This rotation of the shafts in the electric motors is the reason for change in magnetic flux (explained in the next section) within the electric motor.
B)ELECTRICAL ENERGY
2)Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction :
a) Whenever the magnetic flux linked with a circuit changes, an EMF is induced in the
circuit, which lasts as long as the change in magnetic flux associated with the circuit
continues.
b) The magnitude of the induced EMF is equal to the rate at which the magnetic flux
linked with the circuit changes.


(equation of induced EMF in accordance with Lenz’s law)
Where E is the induced Electro Motive Force in Volts and ΦB is the magnetic flux in Webbers.
(equation of EMF induced with N number of loops in a coiled wire).
3) Lenz’s Law:
Whenever an EMF is induced the induced current is in such a direction so as to oppose the change in magnetic flux that produces it. This is the reason for the negative sign in the equation for induced EMF

When the flux through a coil increases, induced EMF tries to oppose that increase by producing an opposing magnetic field. When the flux decreases, induced EMF produces a field to increase the net magnetic flux.
There various methods of inducing EMF in a coil by changing:
- The magnetic field associated with it.
- Changing the area of the coil.
- Angle between the coil and magnetic field by rotation.
We use the third method in our project to induce an EMF inside our electric motor.
4)DC Electric motor and generator:
The principles of electric motor and electric generator are like two sides of a coin:
Electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy whereas, Electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. However, in our project we reverse the working of an electric motor by providing mechanical rotations to its shaft instead of the electric supply through the cables. Here we draw an electric output instead of a mechanical one by supplying a mechanical input instead of electric input. Now our electric motor actually produces 1.5 Volts ! (just enough to light the LEDs). In short, we make use of the DC electric motor as an DC electric generator. The actual working principles of the electric motor and generator are explained below:
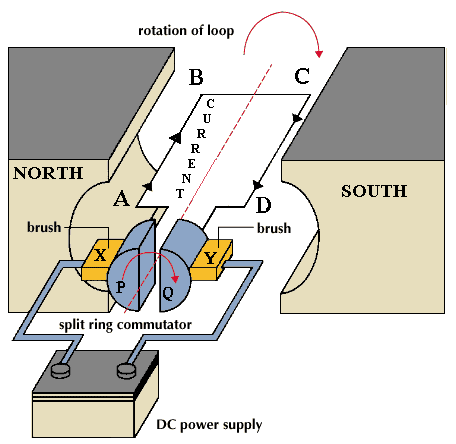
Construction: the main components of dc motor and generator are
a.Armature:
Armature coil (ABCD) consists of a large number of turns of insulated copper
wires wound on soft iron core.
b.Field magnets:
A strong, uniform magnetic field is produced using permanent or electromagnets. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the axis of the armature.
c.Split ring commutator:
reverses the direction of current flowing through the coil after every half rotation of the coil. Due to this the coil continues to rotate in the same direction
d.Brushes:
Two carbon brushes are kept in contact with the slip rings. The brushes are connected to the load through which the induced current flows.
The commercial motors use (i) an electromagnet in place of permanent magnet;
(ii) large number of turns of the conducting wire in the
current carrying coil; and
(iii) a soft iron core on which the coil is wound.
DC Electric Motor:
An electric motor is a rotating device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy.
It works on the principle of Lorentz / Laplace force acting on a wire in uniform magnetic field.